Despite the
development of many protein-based, or biologic, medicines their application has
been limited due to difficulty in administration. An attractive target for
medicinal delivery is macrophage cells, immune cells which attack foreign
materials and pathogens, as the action, or inaction, of these cells are
involved in many diseases. Recently, researchers at Kangwon National University
in Korea utilized PLGA from PolySciTech (www.polyscitech.com)
to deliver protein-based drugs to macrophages. Acid ended PLGA from PolySciTech
(PolyVivo AP081) was conjugated to dopamine to form a nanoparticle which
targeted towards macrophage cells. This
particle was found to be able to deliver a model protein (albumin) to these
cells with high uptake. This research holds promise for treating a wide variety
of diseases ranging from inflammatory disease to cancers. Read more: Lee, Song Yi, and Hyun-Jong Cho.
"Dopamine-conjugated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for
protein delivery to macrophages." Journal of Colloid and Interface Science
(2016). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021979716309559
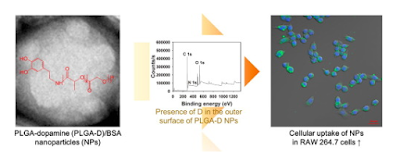
“Abstract: Poly(lactic-co-glycolic
acid)-dopamine (PLGA-D)-based nanoparticles (NPs) were developed for the
delivery of protein to macrophages. PLGA-D was synthesized via amide bond
formation between the –NH2 group of D and the –COOH group of PLGA. Bovine serum
albumin (BSA, model protein) was encapsulated in PLGA NPs and PLGA-D NPs, which
had an approximately 200 nm mean diameter, < 0.2 polydispersity index, and
negative zeta potential value. There was no increment in the mean diameters of
BSA-loaded NPs after 24 h of incubation in biological fluid-simulated media
(i.e., aqueous buffer and serum media). The primary, secondary, and tertiary
structures of BSA released from the NPs were studied by sodium dodecyl
sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDSPAGE), circular dichroism, and
fluorescence spectrophotometry; the structural stability of BSA was preserved
during its encapsulation in the NPs and release from the NPs. PLGA/BSA NPs and
PLGA-D/BSA NPs did not induce serious cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 cells (mouse macrophage
cell line) in an established concentration range. In RAW 264.7 cells, the
intracellular accumulation of PLGA-D NPs was 2-fold higher than that of PLGA
NPs. All of these findings indicated that PLGA-D NPs are a promising system for
delivering proteins to macrophages. Keywords: dopamine; macrophage;
nanoparticles; PLGA; protein”
No comments:
Post a Comment