Optimal use of ligands for active nanoparticle targeting requires selecting the correct antibody to attach to the specific target cell receptor. Recently, researchers at Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology (Spain) and Eindhoven University of Technology, (Netherlands) used PLGA (Cat# AP082) and PLGA-PEG-COOH (Cat# AI078) from PolySciTech (www.polyscitech.com) as part of their research into a quantitative imaging method whereby the optimal ligand is determined prior to nanoparticle preparation by use of direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy. This process was used to apply a systematic and intelligent design to selection of ligands for nanoparticle targeting. This research holds promise to improve therapies against cancer in the future. Read more: Woythe, Laura, Pranav Madhikar, Natalia Feiner-Gracia, Cornelis Storm, and Lorenzo Albertazzi. "A Single-Molecule View at Nanoparticle Targeting Selectivity: Correlating Ligand Functionality and Cell Receptor Density." ACS nano (2022). https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.1c08277
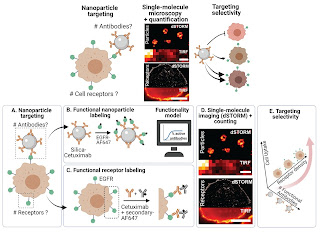
“Antibody-functionalized nanoparticles (NPs) are commonly used to increase the targeting selectivity toward cells of interest. At a molecular level, the number of functional antibodies on the NP surface and the density of receptors on the target cell determine the targeting interaction. To rationally develop selective NPs, the single-molecule quantitation of both parameters is highly desirable. However, techniques able to count molecules with a nanometric resolution are scarce. Here, we developed a labeling approach to quantify the number of functional cetuximabs conjugated to NPs and the expression of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFRs) in breast cancer cells using direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM). The single-molecule resolution of dSTORM allows quantifying molecules at the nanoscale, giving a detailed insight into the distributions of individual NP ligands and cell receptors. Additionally, we predicted the fraction of accessible antibody-conjugated NPs using a geometrical model, showing that the total number exceeds the accessible number of antibodies. Finally, we correlated the NP functionality, cell receptor density, and NP uptake to identify the highest cell uptake selectivity regimes. We conclude that single-molecule functionality mapping using dSTORM provides a molecular understanding of NP targeting, aiding the rational design of selective nanomedicines.”
No comments:
Post a Comment